Notice of the People’s Government of Yunnan Province on Printing and Distributing the Plan of Medical and Health Service System in Yunnan Province during the 14th Five-Year Plan.
State and municipal people’s governments, provincial committees, offices, departments and bureaus:
The "14 th Five-Year Plan" of medical and health service system in Yunnan Province is hereby printed and distributed to you, please implement it carefully.
Yunnan Provincial People’s Government
September 15, 2022
(This piece is publicly released)
Planning of Medical and Health Service System in Yunnan Province during the Tenth Five-Year Plan
In order to further optimize the allocation of medical and health resources in the province, effectively improve the fairness and accessibility of medical and health services, and enhance the ability of all-round life-cycle health services and the level of prevention and treatment of major epidemics, according to the national "14 th Five-Year Plan" medical and health service system plan and the outline of the 14 th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development in Yunnan Province and the long-term goal for the year 2035, the outline of "Healthy Yunnan 2030" and the development plan of health undertakings in Yunnan Province during the 14 th Five-Year Plan
I. Planning background
(A) Development status
During the "Thirteenth Five-Year Plan" period, under the strong leadership of the provincial party committee and the provincial government, our province has continuously deepened the reform of the medical and health system, steadily promoted the construction of a healthy Yunnan, implemented major projects such as the improvement of the ability to treat major infectious diseases and the core competence of disease control institutions, the three-year action plan for the development of health undertakings, and the "seven special actions" for patriotic health. The medical and health service system has been further improved, the service capacity has been significantly improved, and the health level of the people has been continuously improved.
By the end of 2020, there were 26,626 medical and health institutions in the province, including 1,445 hospitals, 24,592 grass-roots medical and health institutions, 532 professional public health institutions and 57 other medical and health institutions. There are 106 tertiary hospitals in the hospital, including 54 tertiary hospitals; There are 470 secondary hospitals, including 196 secondary hospitals. There are 458,900 health workers and 325,200 beds. There are 6.89 beds in medical and health institutions, 2.6 licensed (assistant) doctors and 3.67 registered nurses per thousand people; There are 2.01 general practitioners and 7.5 professional public health personnel per 10,000 population. The construction projects of three national regional medical centers for cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease and tumor have landed in Yunnan, and 30 provincial clinical medical centers and 115 sub-centers have been built, and 16 provinces and cities in the province have achieved full coverage of 3A general hospitals. The number of county-level general hospitals reaching the national basic standards has achieved a historic leap from "0" to "122", and 40 county-level general hospitals have reached the national recommended standards, with the growth rate ranking third in the country. The number of tertiary hospitals in county general hospitals has increased from "0" to "22". 42 counties in the province are listed as the first batch of pilot projects for the construction of close county medical community in China. In 2020, it was selected as a pilot province for the construction of national community hospitals. 73.3% families can reach the nearest medical point within 15 minutes, and the rate of seeing a doctor in the county reaches 91.39%. The proportion of Chinese medicine clinical departments in public general hospitals above the second level is 90%.The setting rate of "Chinese medicine hall" in township hospitals and community health service centers reached 99.35% and 81.4% respectively. The total number of medical and health institutions was 271 million, of which hospitals accounted for 40.13% and primary medical and health institutions accounted for 55.32%. There were 9,704,900 hospitalizations, of which 79.74% were hospitals and 16.68% were primary medical and health institutions. The utilization rate of beds in medical and health institutions is 70.79%, including 77.46% in hospitals, and the average length of stay in hospitals is 8.74 days. The reported incidence of Class A and B infectious diseases has been lower than the national average for 17 consecutive years, achieving the goal of eliminating malaria historically. The completion rates of county-level rescue centers for chest pain, stroke, trauma, critical pregnant women and critical newborns reached 93%, 85%, 80%, 91.47% and 89.92% respectively, ranking among the top in the country. The maternal mortality rate and infant mortality rate dropped to 12.42/100,000 and 4.73‰ respectively, which was better than the national average. The average life expectancy in the province has increased from 69.54 years in 2010 to 74.02 years in 2020, with an average annual increase of 0.45 years, the highest increase in the country. The proportion of personal health expenditure in total health expenditure decreased to 27.07%, which was better than the national average. With practical actions, the Supreme Leader’s General Secretary’s requirements for Yunnan to be a gatekeeper and take responsibility for the country have withstood the continuous impact and severe test of the imported COVID-19 epidemic, and firmly held the bottom line of keeping it secret and preventing a large-scale epidemic.
(B) Opportunities and challenges
The CPC Central Committee with the Supreme Leader as the core has always put people’s life safety and physical health first. The 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China made a major decision of "implementing the strategy of healthy China", which promoted the maintenance of people’s health to the national strategic level. The Fifth Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee clearly put forward the grand goal of basically realizing socialist modernization and building a healthy China by 2035. The basic position and important supporting role of health in the historical process of "two hundred years" are increasingly prominent. Our province is in the critical stage of building a demonstration zone of national unity and progress, a vanguard of ecological civilization construction, and a radiation center facing South Asia and Southeast Asia. The multi-level and diversified health needs of the people will be further stimulated, creating a broader space for the development of health care. The rapid development of new technologies such as artificial intelligence and the fifth generation mobile communication (5G) provides scientific and technological support for optimizing health services and management.
At present, the global epidemic situation in COVID-19 is still in a state of pandemic, and the situation of border epidemic prevention and control in our province is still complicated and changeable. It is urgent to build a strong public health system and enhance the overall ability to deal with public health emergencies. In the face of the sharp increase in the demand for high-quality health services, the further aging of the population and the changes in the disease spectrum, the task of ensuring the health of the whole people in an all-round and full-cycle manner is even more arduous. Problems such as insufficient total quality medical and health resources, uneven distribution and insufficient integration still exist in our province. The number of licensed (assistant) doctors per thousand population and the number of general practitioners per 10,000 population are lower than the national average, and the grassroots capacity is relatively weak and resources are idle. The supply of medical and health services for key groups such as "one old and one small" is insufficient. The cooperation mechanism between various medical and health institutions is not perfect, the level of personnel, technology, equipment, data and information sharing is not high, the integration of medical care and prevention is not sufficient, and the pattern of complementary cooperation between Chinese and Western medicine has not yet formed.
Second, the overall requirements
(A) the guiding ideology
Adhere to the guidance of the Supreme Leader’s Socialism with Chinese characteristics Thought in the new era, thoroughly implement the spirit of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China and the previous plenary sessions of the 19th National Congress, implement the important exposition of the Supreme Leader’s General Secretary on health and health work and inspect the spirit of Yunnan’s important speech, conscientiously implement the decision-making arrangements of the provincial party committee and government, adhere to the general tone of striving for progress while maintaining stability, comprehensively implement the new development concept, thoroughly implement the health and health work policy in the new era, and accelerate the construction of a strong public health system. We will promote the construction of an integrated medical and health service system covering the whole life cycle and the whole health process, and promote the change of development mode from treating diseases to focusing on people’s health, the change of service system from increasing scale and quantity to improving quality and efficiency, and the change of resource allocation from focusing on material factors to paying more attention to talent and technical factors, so as to make the people enjoy a higher level of health services.
(2) Basic principles
Overall planning and system integration. Coordinate the allocation of regional and urban and rural resources, coordinate prevention, treatment, rehabilitation and health promotion, adhere to both Chinese and western medicine, and improve overall efficiency. Combined with population structure and distribution, disease spectrum and other factors, the allocation standards of medical and health resources are formulated by classification.
Demand-oriented, improving quality and expanding capacity. Based on the reality of border areas, ethnic groups and mountainous areas, and guided by major health problems, we will expand the supply of resources, optimize the structural layout, and improve the allocation efficiency. Accelerate the expansion of high-quality medical and health resources and regional balanced layout, narrow the gap in resource allocation and service level among regions, urban and rural areas and people, and consolidate the grassroots foundation.
Coordination of medical care and prevention, and combination of emergency and emergency. Give priority to prevention, combine prevention with treatment, and establish a long-term mechanism of cooperation between medicine and prevention. Based on the usual needs and the need to ensure the prevention and control of major epidemics, we will improve the ability to combine emergency with emergency and quickly switch, and maintain public health safety.
Government-led, diversified participation. Adhere to the public welfare of basic medical and health undertakings, strengthen the responsibility of government investment guarantee, management and supervision, and increase the construction of public medical and health institutions. Give play to the role of market mechanism, encourage and guide social forces to set up medical and health institutions according to law to meet the multi-level and diversified health needs of the people.
Reform and innovation, strengthen support. Continue to deepen the reform of the medical and health system, pay attention to the systematic integration of medical and health resources allocation with policies such as finance, medical insurance and human resources, and give play to the leading and supporting role of talents, science and technology and informatization.
(3) Development goals
By 2025, an integrated medical and health service system will be basically established, which is compatible with the national economic and social high-quality development goals of our province, and compatible with the positioning of China’s radiation center for South Asia and Southeast Asia, with urban and rural planning, complementary functions, regional coordination, high quality and high efficiency. The ability to prevent and treat major epidemics and respond to public health emergencies has been significantly improved, public hospitals have further achieved high-quality development, and the level of medical services has been significantly improved. Grassroots units generally have the ability of first diagnosis and triage and health "gatekeeper", a distinctive Chinese medicine service system has been initially established, the health service ability focusing on "one old and one young" has been significantly enhanced, the basic public health service ability has been significantly improved, and the people’s health level and satisfaction have been continuously improved.
Third, the system structure and resource allocation
Medical and health resources mainly include institutions, beds, manpower, equipment, technology, information and data. Optimize the layout of medical and health resources in the province, make overall planning and balanced layout at the provincial, state and municipal levels, and improve cross-regional service and support capabilities; County-level and grassroots medical and health resources are rationally distributed according to the size of permanent population and service radius.
(1) Institutions
The province’s medical and health service system takes hospitals, grass-roots medical and health institutions and professional public health institutions as the main body, supplemented by new health care service institutions for the elderly, infants and other special groups, and provides life-cycle and health-care services for the whole population, such as disease prevention, treatment, rehabilitation and health promotion.
1. the hospital. Divided into public hospitals and non-public hospitals. Public hospitals are divided into government-run hospitals (divided into provincial hospitals, state-run hospitals and county-run hospitals according to the level of organization) and other public hospitals. Non-public hospitals are an effective way to meet people’s multi-level and diversified medical service needs.
At the provincial, prefecture and county levels, medical institutions at corresponding levels should be set up reasonably according to the number of permanent residents, service scope, workload and other factors in the administrative area, and according to the planning and requirements for the establishment of medical institutions. Guide qualified social medical institutions to develop into large-scale medical groups with high level, high technology content and brand.
2. Primary medical and health institutions. Including township hospitals and community health service centers, community health service stations (points), village clinics, clinics, outpatient departments, etc., to play the role of "double network bottom" for basic medical and public health services.
Grassroots medical and health institutions mainly undertake basic public health services such as preventive health care, health education, disease management, diagnosis and treatment of common diseases and frequently-occurring diseases, and rehabilitation, nursing and hospice care services for some diseases. They receive referrals from hospitals and refer patients beyond their own service capacity to hospitals. Every township should run a government-run health center, every subdistrict office or every 30,000-100,000 residents should set up a community health service center, and reasonably set up community health service stations and village clinics.
3. Professional public health institutions. In principle, it is sponsored by the government, mainly including disease prevention and control institutions, maternal and child health care institutions, emergency centers (stations), blood stations, and specialized disease prevention and control institutions. It mainly provides public health services such as prevention and control of infectious diseases, chronic non-communicable diseases, occupational diseases and endemic diseases, health education, maternal and child health care, pre-hospital first aid, blood collection and supply, and mental health. Scientifically set up disease prevention and control institutions at the provincial, prefecture and county levels. Reasonable establishment of maternal and child health care institutions. With the provincial emergency center as the leader, improve the pre-hospital emergency network at the provincial, prefecture, county and township levels. Set up Yunnan Kunming Blood Center in Kunming, set up a central blood station in the places where the people’s governments of other 15 states and cities are located, and set up at least one fixed blood collection point in each county, city and district. Each state, city, county and district shall set up specialized disease prevention and control institutions as needed.
4. Other institutions. It mainly includes independent institutions and continuous service institutions.
(2) Beds
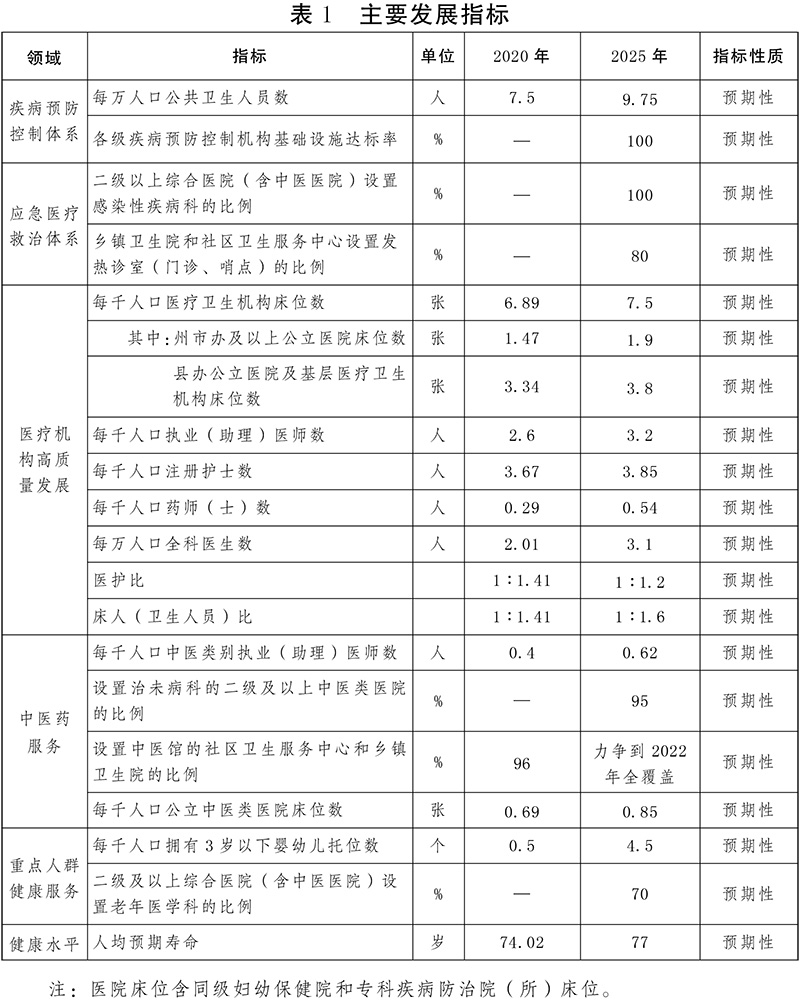
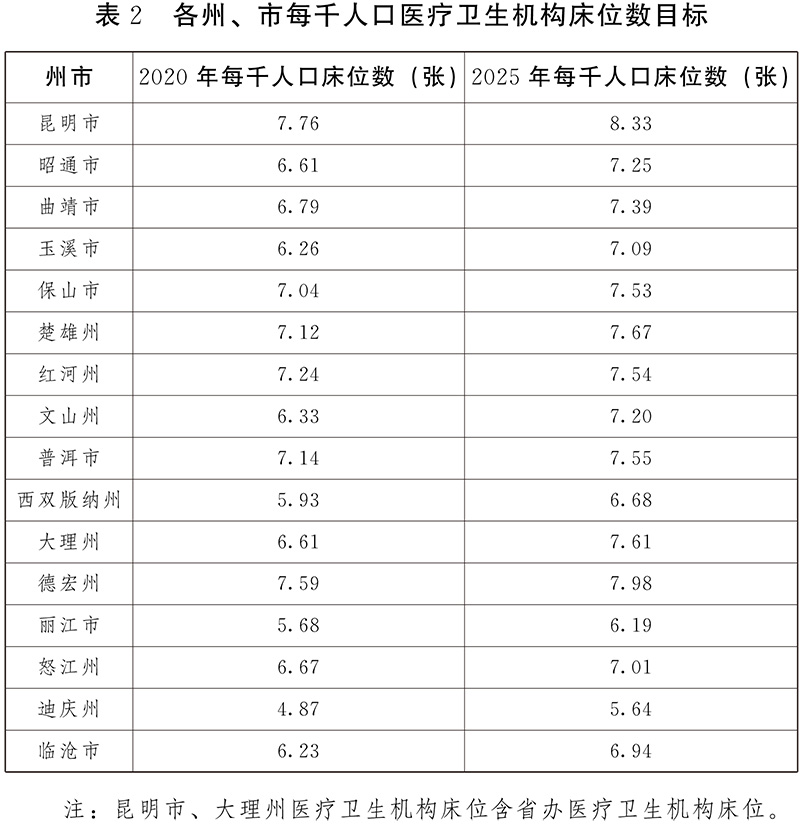
1. Moderately control the bed size. Moderately and reasonably allocate the overall size of beds in provincial, prefecture and county public hospitals, moderately adjust the allocation of beds in high-level and high-quality public hospitals, and guide high-quality medical resources to standardize the setting of branch areas in areas with relatively weak resources. Determine the number and structure of beds reasonably according to the utilization rate of beds at the grass-roots level. By 2025, the expected index of the number of beds in medical and health institutions per thousand people in the province is 7.5 (including 6.2 beds in hospitals and 1.3 beds in primary medical and health institutions such as township hospitals and community health service centers). Among the hospital beds, there are 4.4 public hospitals (including 0.85 Chinese medicine hospitals) and 1.8 non-public hospitals.
2. Optimize the bed structure. Moderately control the growth of treatment beds, and give priority to the shortage areas such as infectious diseases, severe diseases, pediatrics, rehabilitation, mental illness and senile diseases. Combined with bed utilization rate, average length of stay, bed-to-doctor ratio, doctor-to-patient ratio and bed-to-person (health personnel) ratio, moderately control the bed growth rate in Baoshan, Chuxiong, Pu ‘er, Dehong, Nujiang and Diqing; Guide the stable development of beds in Kunming, Zhaotong, Qujing, Honghe and Lijiang; Support Yuxi, Wenshan, Xishuangbanna, Dali and lincang to increase beds reasonably.
3. Improve the quality of bed use. Encourage medical institutions to break the resource management mode with departments as the unit and implement overall deployment of beds in the whole hospital. The utilization rate of beds in public general hospitals is less than 75%, and the average length of stay is more than 9 days. No more beds will be added. Promote tertiary hospitals to pay more attention to the diagnosis and treatment of critical and difficult diseases, gradually reduce the proportion of primary and secondary operations, improve the proportion of appointment referral and daytime operations, and improve the efficiency of bed units.
(3) Manpower
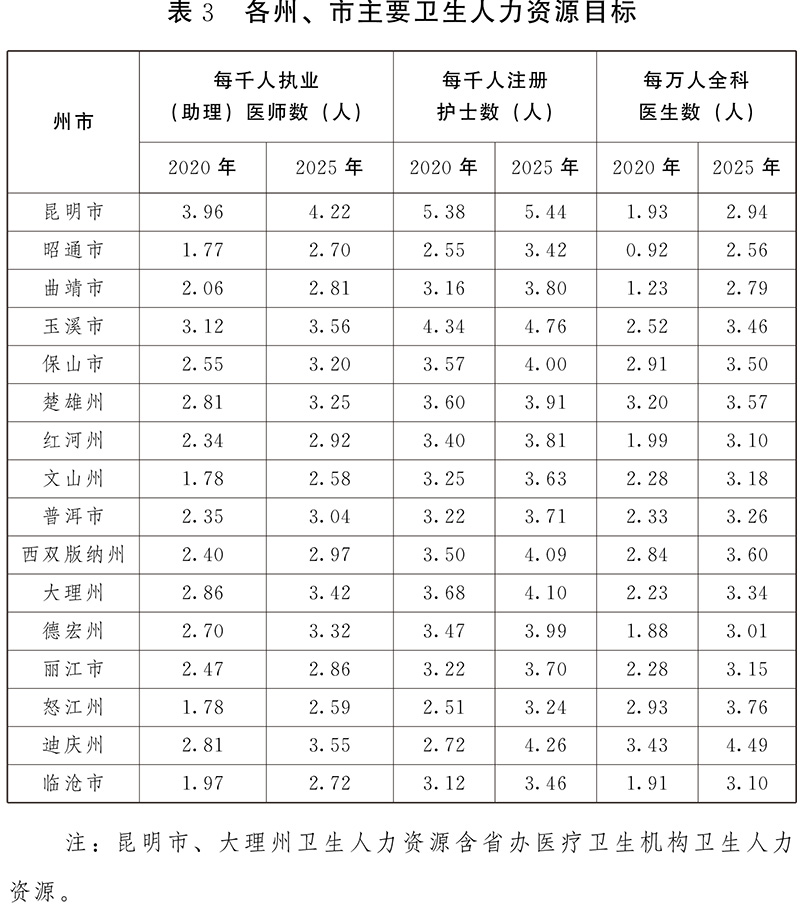
1. Adapt to the changes of disease spectrum and expand the supply of high-quality medical and health services, and guide the rational allocation of medical staff. Guide Zhaotong City, Qujing City, Baoshan City, Honghe Prefecture, Wenshan Prefecture, Pu ‘er City, Xishuangbanna Prefecture, Dehong Prefecture, Nujiang Prefecture, Diqing Prefecture and lincang to increase the growth rate of practicing (assistant) doctors; Zhaotong City, Qujing City, Pu ‘er City, Dehong Prefecture, Lijiang City, Nujiang Prefecture and Diqing Prefecture have increased the growth rate of registered nurses; Kunming, Zhaotong, Qujing, Honghe, Dehong and lincang increased the growth rate of general practitioners.
2. Reasonably improve the allocation standard of public health personnel. In principle, the personnel of disease prevention and control institutions shall be approved according to the proportion of 1.75 people per 10,000 population, and the proportion of professional and technical personnel in the total establishment shall not be less than 85%, and the proportion of health technical personnel in the total establishment shall not be less than 70%. Every 10,000 population is equipped with 1-1.5 health supervisors and 1 health worker in maternal and child health care institutions. Health education institutions, emergency centers (stations), blood collection and supply institutions and other professional public health institutions rationally allocate human resources according to the service population, workload and tasks. In principle, the proportion of professional and technical posts in health education institutions is not less than 80% of the total number of posts, and there are not less than 2 full-time (part-time) staff engaged in health education in various medical and health institutions at all levels. The number of public health personnel in primary medical and health institutions shall not be less than 25% of the number of professional and technical personnel. Community health service centers, township hospitals and medical institutions above the second level are all equipped with at least one public health physician. Promote the transformation of rural doctors into practicing (assistant) doctors. Technical support institutions for occupational disease prevention and control shall be equipped with professional and technical personnel in occupational health, radiation health, testing and inspection, engineering technology, clinical medicine, etc. as required.
3. Improve the allocation of human resources in medical institutions. Reasonably set up posts for different categories of personnel such as doctors, nurses, medicine, technology and management. Hospitals undertaking clinical teaching, teaching practice, supporting grass-roots units, medical research and other tasks, national regional medical centers and provincial high-level hospitals may appropriately increase their staffing. According to national regulations and standards, strengthen the staffing of medical institutions. Strengthen the allocation of general practitioners in township hospitals and community health service institutions.
4. Strengthen the supply of talents in short supply. Increase the proportion of practicing (assistant) doctors in public health, and strengthen the construction of talent teams in the fields of psychiatry, rehabilitation, general practice, severe illness, emergency, anesthesia, stomatology, pediatrics, neonatology, child care, obstetrics, imaging, pathology, geriatrics, occupational health and so on. By 2025, the number of practicing (assistant) doctors and registered nurses in psychiatry per 100,000 population in the province will reach 4 and 8.68 respectively.
(4) Equipment
1. Configuration of medical equipment. Adhere to the sharing of resources and ladder configuration, plan the allocation quantity and layout of large-scale medical equipment in a province as a unit, and guide medical institutions to rationally allocate appropriate equipment. We will implement the reform requirements such as the notification and commitment system for the allocation of Class B large medical equipment by social hospitals and the filing system for the allocation of Class B large medical equipment by social hospitals in the free trade pilot zone.
2. Public health prevention and treatment equipment configuration. According to the needs of ensuring public health safety and referring to relevant national standards, facilities and equipment such as laboratory testing, large-scale rescue, emergency and informatization of professional public health institutions will be configured and updated. Strengthen the equipment configuration of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), mobile CT, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) instrument, mobile operating room, negative pressure ambulance and other medical institutions that undertake the task of treating major infectious diseases and emergency medical rescue.
(5) Technology
1. Promote the development and application of medical technology. Improve the filing management system for clinical application of medical technology, and implement classified and graded management for clinical application of medical technology. Focusing on the people’s medical service needs and major and difficult diseases, we will expand the methods of diagnosis and treatment, improve the medical technical ability and diagnosis and treatment effect, and form a technological advantage. On the basis of ensuring the safety of patients, we encourage the development of cutting-edge technology projects with specialist characteristics and core competitiveness. Strengthen the innovation of clinical diagnosis and treatment technology, applied research and transformation and popularization of results. Strengthen the clinical application evaluation, quality control and management of medical technology.
According to the disease spectrum of residents in our province and the situation of patients seeking medical treatment in different places, we should consider the foundation of specialty construction and population development trend as a whole, focus on serious illness and stay in the province, strive for national key clinical specialty construction projects, implement the construction of upgrading and expanding provincial high-level medical institutions, the construction of provincial clinical medical centers and provincial key specialties, and reduce the rate of patients’ transfer outside the province; Focus on solving common diseases in States, cities, counties and districts, comprehensively improve the core specialty abilities of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, metabolic diseases, pediatrics, mental diseases and infectious diseases, and improve the specialized service system covering common diseases, frequently-occurring diseases and infectious diseases of residents.
2. Strengthen discipline cooperation. Promote multidisciplinary joint diagnosis and treatment for tumors, complicated diseases and chronic diseases. Encourage professional and technical personnel such as anesthesia, medical examination, medical imaging, pathology, pharmacy, rehabilitation medicine and psychiatry to be included in the multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment team, explore the development model of comprehensive disciplines such as heart center, nerve center and tumor center, and improve the comprehensive diagnosis and treatment level of diseases. Encourage medical institutions to set up service coordinators to provide guidance, assistance and follow-up management in patient referral.
(VI) Information and data
Taking the provincial national health information platform as the hub, we will highlight unified data collection, unified use of standards, unified interface formulation, unified application integration and unified resource management, and realize cross-institution, cross-level, cross-regional and cross-departmental interconnection, business collaboration and data sharing of health information, and fully release the potential of big data to support health services and industry governance. Gradually realize the sharing and mutual recognition of electronic medical records, inspection results and medical images among medical institutions. Promote the integration of information systems between medical institutions in the medical community and primary medical and health institutions. Improve the public health service information system. Accelerate the integration of information systems such as electronic health records, family doctors signing contracts, maternal and child health, occupational health, and rehabilitation of the disabled. Promote data integration and business collaboration in public health and medical services. Strengthen the construction of network security.
Fourth, accelerate the construction of a strong public health system
We will strengthen the construction of a public health system with provincial, prefecture and county disease prevention and control institutions and various specialized disease prevention and control institutions as the backbone, medical institutions as the support, and grassroots medical and health institutions as the net, and strengthen the combination of prevention and treatment and the coordination of medical prevention and treatment.
(1) Reform and improve the disease prevention and control system.
1. Focus on responsibilities and enhance core competence. Promote the reform of disease prevention and control system according to the national deployment, and improve the facilities and equipment conditions of disease prevention and control institutions. Strengthen core competencies such as monitoring and early warning, risk assessment, epidemiological investigation and disposal, inspection and testing, emergency response and comprehensive intervention. Accelerate the construction of provincial centers for disease control and prevention-regional centers for disease control and prevention, and strive to build a national regional public health center. Promote the upgrading of laboratory instruments and equipment and the building of biosafety protection capacity in state and municipal centers for disease control and prevention. County, city and district disease prevention and control institutions focus on improving laboratory testing, on-site epidemiological investigation, epidemic situation judgment and on-site emergency response capabilities, and 25 border county and city disease prevention and control centers have upgraded laboratory core capabilities to state-level standards.
2. Promote coordination between medical care and prevention, and improve the efficiency of prevention and control. Public medical institutions set up public health departments and other departments directly engaged in disease prevention and control, and incorporated them into the prevention and control network of infectious diseases and chronic diseases in the territory and the network management of health education promotion. Strengthen the capacity building of infection prevention and control in medical institutions.
Establish and improve the linkage mechanism between disease prevention and control institutions and hospitals, other professional public health institutions, grassroots medical and health institutions and towns (streets). Strengthen the technical guidance, supervision and assessment of disease prevention and control institutions for disease prevention and control in medical institutions. Explore the establishment of disease control supervisor system, and set up full-time and part-time disease control supervisors in hospitals and primary medical and health institutions. Explore the participation of professionals in disease prevention and control institutions in the work of medical complexes.
Taking the management of diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, tuberculosis and severe mental disorders as the breakthrough point, we will train 1-2 compound backbone talents with medical, prevention and management abilities for each township health center, explore equipping grassroots medical and health institutions with intelligent health management equipment, set up scientific fitness clinics in qualified grassroots medical and health institutions, and improve the ability of combining prevention and treatment at the grassroots level.

(two) improve the monitoring and early warning and emergency response system.
1. Improve the monitoring, early warning and emergency response mechanism for infectious diseases and public health emergencies. With disease prevention and control institutions as the main body, hospitals and primary medical and health institutions as the sentinel, supported by information technology and big data technology, a monitoring and early warning mechanism is established to realize early detection, early reporting, early isolation and early disposal of infectious diseases and public health emergencies. Improve the five-level information reporting network of provinces, prefectures, counties, townships and villages. Strive to establish joint workstations or laboratories for infectious disease surveillance with neighboring countries. Improve the information release mechanism of public health emergencies.
2. Improve the ability of emergency response and rapid disposal. Construction of provincial public health emergency command center, unified dispatch and command of the province’s public health emergency disposal work. Strengthen the emergency command system of infectious diseases and public health emergencies at the city and county levels in Quanzhou. Improve the graded emergency response mechanism for infectious diseases and public health emergencies. Improve the health emergency plan system at all levels, strengthen mutual connection, and carry out regular drills to ensure efficient operation. Establish an emergency team and emergency response mechanism for cross-border public health emergencies.
(three) improve the epidemic situation of infectious diseases and major public health emergencies treatment system.
1. Improve the medical treatment system for infectious diseases. We will improve the medical treatment network for infectious diseases at the provincial, prefecture, county and township levels, strengthen the construction of infectious disease hospitals and specialized institutions for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, and improve the comprehensive treatment ability of infectious diseases and the diagnosis and disposal ability of new and recurrent infectious diseases. By 2025, each state and city will have a standardized infectious disease hospital (hospital area), and one infectious disease hospital (hospital area) will be set up in Xuanwei City, Zhenxiong County, Huize County and Guangnan County respectively. Other counties, cities and districts will rely on public general hospitals to plan and construct relatively independent infectious disease wards, and set up negative pressure wards (wards) and intensive care units as required.
2. Build a provincial-level major epidemic treatment base. Relying on the Provincial First People’s Hospital, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, three major epidemic treatment bases will be built. As the diagnosis and treatment center, technical guidance center and remote consultation center of the province, the bases will undertake the centralized treatment of critically ill patients in the province, and respond quickly when major epidemics occur, effectively improving the cure rate of critically ill patients and reducing the mortality rate.
3. Strengthen the emergency medical rescue system. Strengthen the construction of emergency medical rescue institutions and emergency rescue teams, build a three-level rescue system at the provincial, prefecture and county levels, and realize the three-dimensional integration of water, land and air and the integration of Chinese and Western medicine. Accelerate the construction of national emergency medical rescue base. Establish regional emergency medical rescue centers in Zhaotong City, Honghe Prefecture, Pu ‘er City, Dali Prefecture, Lijiang City and other States and cities, and other States, cities, counties and districts make overall arrangements to build emergency medical rescue sites. Promote the construction of aviation and water emergency medical rescue system. Emergency departments are set up in general hospitals above the second level to strengthen the effective connection between pre-hospital medical emergency and in-hospital emergency.
Five, accelerate the construction of high-quality medical service system.
We will build a high-level public hospital network based on national regional medical centers and provincial key hospitals, with state-run hospitals as the backbone and county-run hospitals as the foundation. Promote the expansion and sinking of provincial key hospitals, support state, city and county hospitals to improve their comprehensive service capabilities, and promote the high-quality development of the province’s medical service system.
(A) the construction of medical services highland
1. Pay close attention to the construction of national regional medical centers. We will build national regional medical centers for cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases and tumors, strive for more national regional medical centers for trauma and neurology, and build a highland of regional medical services integrating high-level clinical diagnosis and treatment centers, high-level clinical scientific research innovation platforms and high-level talent training bases. On the basis of building national regional medical centers, we will promote the construction of provincial regional medical centers, promote the rapid improvement of the overall medical level in our province, and strive to basically solve critical and difficult diseases in the province.
2. Accelerate the improvement of the capacity of provincial hospitals. Focusing on diseases with high mortality rate and high external transfer rate in the province, we will speed up the construction of provincial clinical medical centers, implement the "excellent training project", support provincial-run hospitals to strengthen the construction of characteristic specialties, platform specialties and weak specialties, enhance the provincial diagnosis and treatment capacity, and reduce cross-provincial medical treatment.
(2) Accelerate the improvement of the medical service capacity of state-run hospitals.
Support and guide the export of high-quality medical resources inside and outside the province to States and cities, support the cooperation between States and cities and domestic high-level medical colleges, accelerate the construction of provincial clinical medical center sub-centers and national key clinical specialties and provincial key clinical specialties, build regional centers with strong leading and radiation-driven functions, and significantly narrow the gap between the diagnosis and treatment level of key diseases and provincial capital cities. Piloting the construction of compact urban medical groups. By 2025, at least one tertiary public general hospital in each of the 14 states and cities will meet the basic standard requirements of the medical service capability guidelines for tertiary general hospitals.
(3) Consolidate and improve the comprehensive capacity of county-level hospitals.
Relying on county-level hospitals to build "five centers" for clinical services and "five centers" for emergency treatment. We will comprehensively promote the construction of a compact county medical community, and set up "five centers" for sharing county medical resources and "five centers" for high-quality management of county medical communities. Support some public hospitals in border counties and cities to moderately increase their bid and expand their capacity. Improve the service capacity of provincial and county-level public hospitals in Zhaotong City, Qujing City, Chuxiong Prefecture, Wenshan Prefecture, Lijiang City, Diqing Prefecture and other cities, and reduce the rate of visits outside the provincial counties.
(4) Continuously improve the comprehensive service capacity of primary medical and health institutions.
We will promote the improvement of the comprehensive service capacity of primary medical and health institutions, optimize the functions of basic medical and public health services, and build a network for the prevention and control of normalized epidemics at the grassroots level. Promote some township center hospitals with large service population, large scale and strong service capacity to gradually reach the service capacity of secondary hospitals on the basis of meeting the national service capacity recommendation standards. Guide the general township hospitals to do a good job in emergency first aid and daily diagnosis and treatment of common diseases, focus on building 1-2 high-quality characteristic departments, and expand and improve service functions. Accelerate the expansion of specialized medical services such as rehabilitation, pediatrics, and dentistry to meet the needs of the people for medical services and diversified health services. Strengthen the construction of community health service centers, improve the level of basic public health services and comprehensive service capabilities such as diagnosis, treatment, nursing, rehabilitation treatment and rehabilitation training for common and frequently-occurring diseases. Support mature community health service centers and township hospitals to establish community hospitals.

(5) Guide the coordinated development of non-public medical institutions.
Standardize and guide social forces to set up independent medical institutions, strengthen standardized management and quality control, and improve the level of homogenization. Encourage the large-scale and brand development of medical services in society. Support non-public medical institutions to cooperate with public hospitals in medical business, discipline construction and personnel training, and join urban medical groups, close county medical communities, specialist alliances and telemedicine networks. Social hospitals will be integrated into the prevention and control of infectious diseases and the medical treatment system for public health emergencies according to law.
Six, strengthen the construction of traditional Chinese medicine (ethnic medicine) service system.
We will improve the service system of traditional Chinese medicine, with provincial hospitals of traditional Chinese medicine as the leader, hospitals of traditional Chinese medicine at all levels and departments of other medical institutions as the backbone, and grass-roots medical and health institutions as the foundation, integrating prevention, health care, disease treatment and rehabilitation.
(A) improve the medical service system of traditional Chinese medicine
We will strengthen the construction of provincial-level Chinese medicine hospitals, and state and municipal Chinese medicine hospitals will meet the construction standards of tertiary Chinese medicine hospitals, and the county-level public Chinese medicine medical institutions will be fully covered. Relying on the Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, we will build a provincial ethnic medical hospital and strengthen the construction of medical systems for Dai, Yi and Tibetan ethnic groups. Accelerate the upgrading and capacity expansion project of county-level Chinese medicine hospitals. Support medical institutions at all levels to build a famous yiguang and a Chinese Medicine Hall. Strengthen the construction of Chinese medicine departments in general hospitals, specialized hospitals, maternal and child health hospitals and other institutions, and strengthen the allocation of Chinese medicine doctors in clinical departments. Promote the full coverage of the construction of "Chinese Medicine Museum" in township hospitals and community health service centers. Support social forces to set up Chinese medicine medical institutions.
(B) to enhance the ability of Chinese medicine services
Support provincial hospitals of traditional Chinese medicine to build high-level hospitals, support the construction of key hospitals with characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine in cities and prefectures, implement the plan of improving the quality of county-level hospitals of traditional Chinese medicine, implement the project of cultivating advantages with characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine, strengthen the construction of five provincial clinical medical centers of traditional Chinese medicine and 32 sub-centers of cities and prefectures, and implement the construction of key clinical disciplines of traditional Chinese medicine at the provincial level. Do well and strengthen the traditional advantages of traditional Chinese medicine specialties such as bone injury, anorectal diseases, pediatrics, dermatology, gynecology, acupuncture, massage, tumor, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, lung diseases, spleen and stomach diseases, nephropathy, peripheral vascular diseases, and support the construction of key specialties of ethnic medicine such as Dai, Yi and Tibetan. Support the construction of TCM specialist alliance, and improve the development level of homogenization of specialties (disciplines). Promote the implementation of the "prevention of disease" project of traditional Chinese medicine, expand the service connotation, and explore the establishment of a number of standardized prevention and treatment departments.
(3) Promoting the coordinated development of Chinese and Western medicine
Strengthen the work of traditional Chinese medicine in general hospitals and maternal and child health care institutions, continuously improve the clinical cooperation mechanism between Chinese and Western medicine, incorporate Chinese medicine into the multidisciplinary consultation system, and organize collaborative research on major and difficult diseases, emerging infectious diseases and chronic diseases. Strive for state support to build 1-3 "flagship" hospitals, build a number of "flagship" departments, build a number of provincial-level collaborative bases of Chinese and Western medicine, and screen and launch a number of collaborative clinical diagnosis and treatment programs of Chinese and Western medicine.
(D) to enhance the ability of Chinese medicine disease prevention and control.
Relying on the provincial hospital of traditional Chinese medicine, we will build a national TCM epidemic prevention base and a national TCM emergency medical team. Relying on universities and enterprises to establish a basic research and industrial innovation platform for the prevention and treatment of epidemics in traditional Chinese medicine. Promote the establishment of fever clinics in tertiary Chinese medicine hospitals and conditional secondary Chinese medicine hospitals, and strengthen the construction of weak departments such as infectious diseases, critical care medicine (emergency department) and pulmonary diseases, and convertible infectious diseases and intensive care units in Chinese medicine hospitals.
Building a scientific research support platform for Chinese medicine to deal with public health emergencies. Increase the research and development of new drugs and preparations for medical institutions to prevent and treat major infectious diseases with traditional Chinese medicine. We will build a team of experts in emergency treatment of traditional Chinese medicine at the provincial, prefecture and city levels, and formulate and improve a number of Chinese medicine prevention and control programs for major infectious diseases.
Seven, improve the all-round and full-cycle health service system.
Focusing on the whole life cycle and the whole process of health, focusing on "one old and one young", we will speed up the improvement of maternal and child health, elderly health, occupational health, mental health and blood supply security service systems, fill the shortcomings in health education, rehabilitation medical care, long-term care for the elderly and hospice care, establish and improve the policy standard system and service supply system for infants under 3 years old, and comprehensively improve the all-round and full-cycle health service capacity.
(A) the development of universal care service system
Gradually establish and improve the policy standards and service supply system to promote the development of infant care services, carry out various forms of infant care services, and gradually meet the needs of the people for infant care services. Support and promote infant care services, strengthen support and guidance for family infant care, strengthen the functional connection between community infant care service facilities and public service facilities, and give full play to comprehensive benefits. Guide social forces to organize inclusive infant care service institutions. Encourage employers to provide welfare infant care services, support kindergartens to set up nursery classes, expand the supply of infant care services, and build a number of pilot infant care services with demonstration and driving effects.
(B) optimize the maternal and child health service system
1. Improve the maternal and child health service network. Improve the maternal and child health service network with maternal and child health institutions as the backbone, general hospitals and specialized hospitals as the support, and basic medical and health institutions as the foundation, promote the combination of health care and clinic, and enhance the supply capacity of maternal and child health services. Support the construction of the new hospital of the Provincial Maternal and Child Health Hospital (Provincial Women and Children Hospital) and strive to build a regional maternal and child health radiation center for South Asia and Southeast Asia. Take state and county-level maternal and child health hospitals as the main body of construction, and strive to reach the standard level of third-level maternal and child health hospitals by 2025; More than 60% of county-level maternal and child health hospitals meet the standards of secondary maternal and child health hospitals.
2. Provincial, state and municipal centers for the treatment of critically ill pregnant women and newborns should be upgraded. Relying on comprehensive hospitals with strong comprehensive treatment capacity and maternity and child care hospitals with outstanding obstetrics and pediatrics strength, and establishing multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment cooperation mechanisms with other medical institutions, we will build and improve the treatment capacity of 20 provincial-level treatment centers for critically ill pregnant women and critically ill newborns; At least one rescue center for critically ill pregnant women and one rescue center for critically ill newborns should be set up at the state, city and county levels.
3. Improve the birth defect prevention network. Improve the prevention and control system of birth defects covering urban and rural residents and the whole process of birth. One or two provincial prenatal diagnosis centers have been set up at the provincial level, and 60% of the states and cities have at least one prenatal diagnosis institution. Pre-marital health care, pre-pregnancy health care, prenatal screening, neonatal genetic and metabolic diseases screening, neonatal hearing impairment screening and neonatal congenital heart disease screening are widely carried out in counties, cities and districts. Strengthen the role of grassroots medical and health institutions in the publicity and mobilization of birth defect prevention and health education.
4. Improve the children’s health service network. Promote the construction of provincial pediatric projects, focusing on improving the ability of children to treat diseases such as respiration, nerves, blood and tumors. States and cities with large populations should set up children’s hospitals or children’s medical centers in general hospitals. At least one hospital in each county, city and district has an independent pediatrics department. By 2025, there will be 0.87 pediatric practicing (assistant) doctors and 2.5 beds for every thousand children in the province. Strengthen the construction of primary child health care service network.
(3) Strengthening the health service system for the elderly
1. Improve the geriatric medical service network. With general hospitals and geriatric hospitals with geriatric departments as the main body, and basic medical and health institutions, nursing institutions and hospice care institutions as the basis, we will improve the four-level health service network for the elderly at the provincial, prefecture, county and township levels, provide the trinity of "prevention, treatment and care" and promote the transformation of health service for the elderly from a disease-centered single-disease model to a health-centered multi-disease co-treatment model. Improve the ability of geriatric medical services in primary health care institutions and promote the extension of geriatric health services to communities and families.
2. Deepen the combination of medical care and nursing. Reasonable layout of continuous medical institutions and pension institutions, improve the cooperation mechanism between medical and health institutions and pension service institutions. Promote the construction of provincial geriatric hospitals. Accelerate the construction of friendly medical institutions for the elderly. Carry out the demonstration work of combining medical care with nursing care.
3. Strengthen long-term care and hospice care services. Increase the supply of long-term care service resources, and establish and improve the elderly care network based on institutions, communities and homes. Relying on qualified nursing homes (centers, stations), community health service centers, township hospitals and other medical and health institutions to set up family beds, community day care centers and "call centers." Promote the synchronous setting and supporting construction of nursing stations, community pension service facilities and elderly care service institutions. We will steadily expand the trial of hospice care. Strive to build a provincial-level hospice training base. Build a standardized hospice ward in each county, city and district of the national hospice pilot state and city, and set up hospice beds in qualified township hospitals (community health service centers). Support social forces to standardize hospice care services.
(D) Improve the technical support system for occupational health.
Gradually establish a technical support network for occupational disease monitoring and evaluation at the provincial, prefecture and county levels. Improve the supporting capabilities of occupational diseases and occupational hazard factors monitoring, occupational health risk assessment, statistics and investigation and analysis of occupational disease prevention and control, occupational health examination, occupational disease reporting and emergency response in the province.
Through independent construction or joint construction of "consortium" and other forms, the technical guidance center and research base of occupational disease hazard engineering protection in Yunnan Province will be built. Establish a technical support platform for engineering protection against occupational hazards in line with the characteristics of major industries in our province.
Relying on occupational disease specialist hospitals and general hospitals, we will build a technical support network for occupational disease diagnosis and treatment at the provincial, prefecture and county levels, and extend it to key towns (streets). Relying on qualified state, city and county general hospitals (general hospital occupational disease specialist), carry out occupational disease diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation. In towns (streets) where pneumoconiosis patients are concentrated, pneumoconiosis rehabilitation stations (points) are established relying on primary medical and health institutions. Support relevant professional organizations to participate in the technical support network for occupational disease prevention and control. Set up full-time and part-time occupational disease prevention supervisors in primary medical and health institutions.
(5) Improve the health education system.
Improve the health education network composed of health education professional institutions, health education service bases, various medical and health institutions and health education functional departments of organs, schools, communities, enterprises and institutions, so as to provide strong system support for health promotion. Promote the construction of health education departments in hospitals, professional public health institutions and grassroots medical and health institutions at all levels, and improve the health education service capacity of medical and health institutions. Mobilize more social forces such as institutions, schools, communities, enterprises and institutions, and health industry associations to participate in the popularization of health knowledge.
(six) improve the mental health and mental health service system.
We will improve the mental health and mental health service system with mental health prevention and control centers at all levels, psychiatric departments of specialized mental hospitals and general hospitals as the main body, grassroots medical and health institutions and psychiatric rehabilitation institutions as the support, and disease prevention and control institutions and social and psychological service institutions as the supplements, so as to provide people with mental health and mental illness prevention, intervention, treatment and rehabilitation services.
1. Improve mental health service capacity. Strive to build a national clinical medical research sub-center in the field of mental illness. Encourage psychiatric hospitals to form or participate in the construction of specialist alliances. Encourage qualified psychiatrists to set up full-time or part-time psychiatric clinics. Township hospitals and community health service centers (stations) should set up psychiatric (psychological) clinics to improve the ability of grassroots mental (psychological) health services. Improve the community rehabilitation system for mental disorders supported by mental health professional institutions, community rehabilitation institutions, social organizations and families. Encourage social forces to hold non-profit psychiatric hospitals and open psychiatric clinics in areas with weak resources for psychiatric medical services.
2. Establish a social mental health service network covering urban and rural areas. Relying on the provincial mental health center and the conditional mental specialist hospitals or psychiatric departments of general hospitals in various states and cities, a public health emergency psychological rescue center will be established, and a psychological rescue team for public emergencies at the provincial, state and county levels will be established. Strengthen the mental health service capacity of medical and health institutions. Relying on urban and rural community comprehensive service facilities or grass-roots comprehensive management centers, standardize the setting of psychological counseling (counseling) rooms or social studios (stations), and equip psychological counselors or social workers. Support the cultivation of professional and standardized psychological counseling and counseling institutions and undertake mental health services.
(7) Strengthening the rehabilitation medical service system.
Improve the rehabilitation medical service network based on rehabilitation departments and rehabilitation hospitals in general hospitals and basic medical and health institutions. The rehabilitation department of tertiary hospitals and tertiary rehabilitation hospitals focus on providing rehabilitation medical services for patients with critical and complicated diseases, and undertake tasks such as rehabilitation medical technology, scientific research and teaching, discipline construction, department management, personnel training, and the transformation, popularization and application of research results in the region. The rehabilitation departments of secondary hospitals, secondary rehabilitation hospitals, rehabilitation medical centers and primary medical and health institutions focus on providing rehabilitation medical services for patients with definite diagnosis, stable condition or long-term rehabilitation. Encourage the development of community and home rehabilitation medical services based on grassroots medical and health institutions.
Support the transformation and reconstruction of some primary and secondary hospitals in areas rich in medical resources into rehabilitation hospitals. Strengthen the supply of rehabilitation medical services for the elderly, and maternal and child health care institutions and children’s hospitals have the ability to provide rehabilitation services for women and children. Strengthen the rehabilitation infrastructure construction and equipment configuration of primary medical and health institutions, and encourage qualified primary medical and health institutions to set up or increase beds to provide rehabilitation medical services according to demand. Implement the Chinese medicine rehabilitation service capacity improvement plan. Support qualified medical institutions to strengthen cooperation with professional rehabilitation institutions for the disabled and improve the level of rehabilitation. Support and guide social forces to organize large-scale and chained rehabilitation medical centers. Strengthen the construction of rehabilitation medical service talents. By 2025, there will be 8 rehabilitation doctors and 12 rehabilitation therapists per 100,000 population in the province.
(eight) optimize the blood collection and supply service system.
Construct a blood collection and supply service system with reasonable layout and efficient operation. Promote the standardization and standardization of blood centers in Kunming, Yunnan Province and blood centers in 15 prefectures and cities, and standardize the setting of apheresis plasma stations in accordance with the Planning for the Setting of Apheresis Plasma Stations in Yunnan Province (Yunwei Yifa [2021] No.27). By 2025, the service capacity of blood stations at all levels will be significantly improved.

Eight, strengthen the support system
(1) Deepening reform in key areas.
Adhere to and strengthen the Party’s overall leadership over public hospitals, and strengthen innovation in system, technology, mode and management of public hospitals. Optimize the performance evaluation of public hospitals, establish and improve the comprehensive performance evaluation system of compact county medical community (compact city medical group) with health as the center, strengthen the application of evaluation results, and promote the high-quality development of public hospitals.
Learn and popularize Sanming’s medical reform experience, and increase the joint efforts of medical care, medical insurance and pharmaceutical reform. We will steadily and orderly promote the reform of medical service prices and implement the dynamic adjustment mechanism of medical service prices. Improve the price policy and medical insurance payment policy for Chinese medicine services and "Internet+medical services". Improve the medical insurance payment policy for medical treatment of major epidemics, and establish and improve the mutual aid guarantee mechanism for employees’ medical insurance clinics. We will implement a multi-compound medical insurance payment method based on disease payment, and improve the payment method and settlement management mechanism of medical insurance funds that adapt to the development of medical services.
We will implement the centralized drug procurement organized by the state, improve the supporting incentive and restraint mechanism for centralized drug procurement, implement the policy of retaining the balance of medical insurance funds, and give priority to the use of drugs selected in centralized drug procurement. Establish and improve the linkage management mechanism of drugs such as urban medical associations and county medical associations. Continue to consolidate and improve the basic drug system, and promote medical institutions at all levels to gradually form a "1+X" medication model dominated by basic drugs. Select and build a provincial clinical pharmacy center to speed up the "standardization, standardization, institutionalization, informationization and homogenization" of pharmaceutical services in the province. We will improve the linkage mechanism of consultation on drug supply security in short supply, and improve the monitoring, early warning and grading response system for drug shortage at the provincial, prefecture and county levels. Strengthen the construction of drug use monitoring system. The application scope of drug use monitoring basically covers secondary and above public medical institutions, and extends to more than 80% of grassroots public medical institutions. Establish and improve the assessment mechanism for rational drug use in medical institutions. By 2023, the assessment coverage of secondary medical institutions will be achieved, and the assessment coverage rate of primary medical and health institutions will reach more than 50% and increase year by year. Promote the pilot work of clinical comprehensive evaluation of drugs.
(B) to strengthen the construction of talent team
Fully implement the "Thirty Measures to Promote the Development of Health Talents in Yunnan Province". Improve the talent evaluation and professional title evaluation mechanism that meets the characteristics of the medical and health industry. Continue to strengthen the training of practicing (assistant) doctors. Promote the access system for public health doctors, implement the system of public health chief experts, explore giving public health doctors the right to prescribe, and promote the pilot program of standardized training for public health doctors. Improve the standardized training system for residents and implement the "two equal treatments". Promote the pilot of standardized training for specialists, and coordinate the implementation of assistant general practitioner training. We will continue to carry out free training of rural order-oriented medical students, do a good job in employment placement and performance management of oriented medical students, strengthen the training of professionals in short supply at the grassroots level, and continue to carry out education for upgrading the academic qualifications of grassroots personnel. Strengthen continuing medical education. Strengthen the training of international medical and health personnel, build a training base for medical and health personnel in South Asia and Southeast Asia, train a group of international talents who know their major and can speak foreign languages, and train suitable health management and professional and technical personnel for neighboring countries. Strengthen the training of talents with Chinese medicine characteristics, implement the provincial-level training program for outstanding clinical talents of Chinese medicine, promote the establishment of a three-level teacher-training system at the provincial, prefecture and county levels, build a group of famous and old Chinese medicine experts’ inheritance studios, and cultivate a group of traditional Chinese medicine talents; Promote the establishment of the system of western learning, and train a group of high-level talents of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine and general practitioners who can provide integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine services.
(3) Strengthening scientific research and innovation
Combined with the forefront of international development, according to the demand and development trend of medical and health services in the province, we will support interdisciplinary integration and innovate in the fields of major disease prevention and treatment, drug abstinence, plateau dermatosis, geriatrics, cross-border public health issues, ecological civilization construction and health that affect the health level of our province.
Improve the layout of medical research bases, focus on solving major health problems, strengthen cooperation with universities and research institutions, and strengthen the construction of compound innovation teams. Strengthen inter-agency, inter-departmental and interdisciplinary cooperation, improve the evaluation and transformation system of scientific and technological achievements, and strive for 1-2 provincial high-level hospitals or professional public health institutions to enter the national clinical medical research center or collaborative innovation network.
Accelerate the construction of scientific research innovation platforms, key laboratories, engineering centers, provincial clinical medical research centers (sub-centers), national clinical medical centers (sub-centers) and academician expert workstations. Strengthen the construction of national clinical research base of traditional Chinese medicine and traditional Chinese medicine inheritance and innovation center.
Nine, improve the planning implementation mechanism
(A) to strengthen organizational leadership
We will comprehensively strengthen Party building in medical and health institutions, and implement the Party’s leadership in all fields and all aspects of health care reform and development. Strengthen the government’s responsibility, and put the formulation and implementation of the medical and health service system planning into the important agenda of the government’s work and the task requirements of building a healthy Yunnan. The provincial people’s government is responsible for formulating provincial plans, refining the bed allocation standards to States and cities, clarifying the layout of provincial high-level hospitals and regional disease prevention and control centers, and incorporating them into the regional health planning of the state and city where they are located. The people’s governments of prefectures and cities are responsible for studying and formulating regional health plans and organizing their implementation, focusing on planning hospitals and professional public health institutions at or below the prefecture level, and refining the bed allocation standards to counties, cities and districts. County, city and district people’s governments are responsible for the formulation and implementation of the county medical and health service system planning, and timely connect with the relevant departments of the state and city.
(2) Strengthen departmental coordination
Institutions, development and reform, education, science and technology, finance, human resources and social security, natural resources, health, medical security and other departments should conscientiously perform their duties, strengthen policy coordination, and make overall plans to promote the implementation of the medical and health service system. The organization department shall implement the staffing of public medical and health institutions in accordance with relevant regulations and standards; The development and reform department should carry out capital construction management and implement capital construction investment for new (expanded) construction projects according to the medical and health service system planning; The financial department should implement relevant funds in accordance with the government’s health investment policy; Natural resources departments should make overall consideration of the development needs of medical and health institutions in the land and space planning, rationally arrange the layout of land use, and give priority to ensuring the land use of non-profit medical and health institutions within the scope permitted by laws and regulations; The health department should take the lead in adjusting the planning according to the procedures as needed; Medical security departments should work together to promote the reform of medical service price and payment system; Other relevant departments should carry out their duties and jointly promote the planning and implementation of the medical and health service system.
(3) Strengthen investment guarantee
Establish a stable investment mechanism for the construction of medical and health service system. Expenditure on the development and construction of professional public health institutions, such as capital construction, equipment purchase, discipline construction and personnel training, shall be fully arranged by governments at all levels according to the needs of public health development; Personnel funds, public funds and business funds are fully arranged in the government budget according to personnel standards, funding standards, service task completion and assessment; Improve the funding guarantee mechanism for public health services in medical and health institutions. Establish a long-term financial input mechanism for emergency reserves of infectious diseases and public health emergencies, and incorporate them into the government’s regular budget arrangements. Implement the government’s responsibility to invest in public hospitals that meet the regional health planning, and implement the investment tilt policy for traditional Chinese medicine hospitals and specialized hospitals such as infectious diseases and mental diseases. Comprehensively strengthen the government’s investment guarantee for primary medical and health institutions. Explore ways to strengthen financial support for the development of childcare services through institutional operating subsidies, family childcare subsidies, and government procurement.
(D) Mobilizing social participation
Combined with the implementation of township (street) power and responsibility list system, strengthen and clarify the power and responsibility of township (street) public health management, village (neighborhood) committees promote the construction of public health committees. The school set up a health department (clinic) in accordance with the regulations, equipped with full-time and part-time health technicians, and implemented the physical examination of freshmen and the screening of key diseases for teachers and students. The employer shall do a good job in the prevention and control of diseases among employees. Improve the linkage mechanism between disease prevention and control departments and urban and rural communities, and build a grass-roots governance mechanism that dynamically connects normal management and emergency management. Strengthen the construction of patriotic health organizations, guarantee the establishment of institutions, functional allocation and staffing, improve the patriotic health work network at all levels, and clarify the full-time and part-time patriotic health workers in towns (streets), villages (communities), organs, enterprises and institutions. Improve the social health education network and mobilize social forces to participate in the popularization of health knowledge.
(5) Strengthen monitoring and evaluation.
The health department should take the lead in establishing a monitoring and evaluation mechanism for the planning of medical and health service system and the efficiency of resource allocation, set up a special working group, organize the dynamic evaluation of the implementation progress and effect of the planning of medical and health service system, carry out the mid-term and final evaluation of the planning on schedule, accept social supervision, find and solve problems in the implementation of the planning in time, and ensure the smooth completion of all objectives and tasks.